The polar vortex broke; what that means for your weather
What is the polar vortex? How it can impact snow, freezes in the U.S.
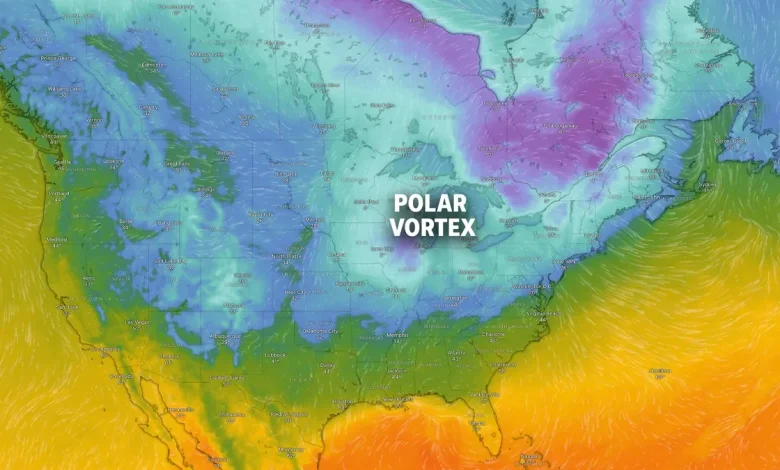
The polar vortex is a large area of circulating cold air above the North Pole. Strong winds keep it contained, but when it weakens, it can wobble and stretch.
The polar vortex has broken, and severe temperatures are set to dominate most of the country in the coming days. Temperatures in the 10s are forecast for much of the Northeast, and subzero temperatures are expected to freeze most of the Midwest and Northern Plains through most of December.
But what is a polar vortex, and what does it mean when it breaks? Here’s what to know:
What is a polar vortex?
Cold, Arctic air is severe. Fortunately, year-round, that air is usually kept tightly contained in the North Pole.
Arctic wind patterns create a sort of wall around the pole that prevents frigid air from trickling southward. That wall that keeps cold air contained is called polar vortex.
Commonly, though, people refer to polar vortex when that retaining wall breaks or weakens and Arctic air slips out of the pole and into other regions.
Polar vortices happen in both, the North and the South Pole.
What causes the polar vortex to break and let cold air move?
The two main causes area sudden warming of the Earth’s stratosphere, and lack of strong wind activity around the pole.
Strong polar winds creates a strong vortex which keeps cold air trapped at the pole. And weak polar winds weakens the vortex which allows cold air to spill southward.
When that happens, Arctic air chills temperatures in other regions.
Juan Carlos Castillo is a New Jersey-based trending reporter for the USA Today Network. Find him on Twitter at _JCCastillo.





